Custom promotion development
The promotion engine in EPiServer Commerce is built on the Windows Workflow Rules Engine. EPiServer Commerce comes with several custom promotions which use this engine. In addition, you can create your own promotions accessing the promotion engine. This section explains the main steps when developing and testing customized promotions.
Classes referred to here are available in the following namespaces:
- Mediachase.Commerce.Orders
- Mediachase.Commerce.Workflow.Activities.Cart
- Mediachase.Commerce.Website.Helpers
- Mediachase.Web.Console.BaseClasses
- Mediachase.Commerce.Marketing.Dto
- Mediachase.Commerce.Marketing.Validators
Refer also to Promotions and Creating a Volume Discount Promotion for related information.
How it works
There are two things that need to be built when creating a new promotion:
- A configuration file to create an experssion or "template", for a promotion.
- A configuration control to allow users to create as many unique instances of the promotion from the template as they want in Commerce Manager.
For example, you might create an expression (template) for a promotion where:
- When a shopper buys product X...
- ...the price of product Y will be reduce by Z percent
Once this expression (template) is created, a configuration control is created to allow users to configure promotions from this template in Commerce Manager. Think of the template as a formula with variables which constitute the promotion and the configuration control as the place to set the value of the variables. The promotion engine calculates the discounts applicable to a cart based on the promotions created in Commerce Manager.
Before developing a promotion, several things should be considered. One is whether there is an existing promotion built-into EPiServer Commerce that accomplishes most of what you already want to do. For most new custom promotions, built-in promotions will include most of the functionality needed. Often copying an existing promotion to create a new promotion will provide 70-90% of the needed logic. Another consideration is that the design of the promotion should be clear before you start developing it.
Creating the configuration control
It is easiest to begin by developing the configuration control. When completed, the configuration control will provide the logic and user interface, which will allow users to set the variable values for the promotion rules template (expression). In this example, the control will be displayed under "Purchase Conditions and Rewards" in the image.
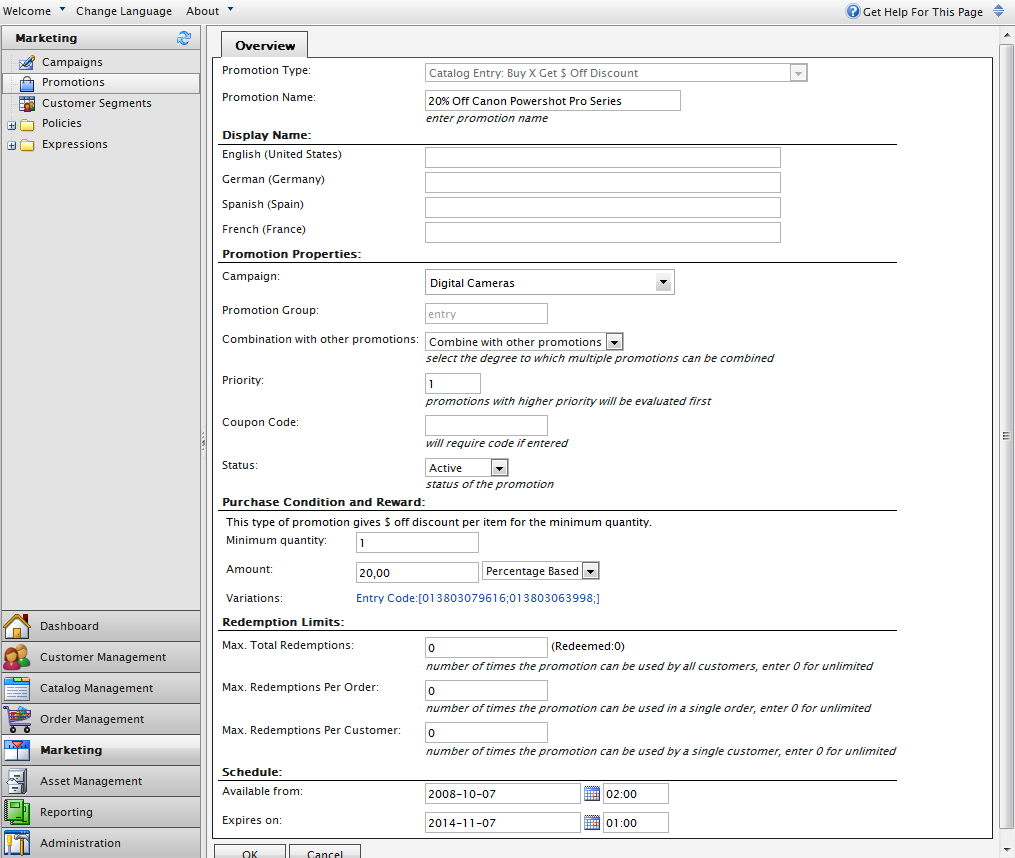
There is a general pattern for elements in the configuration control:
- The control needs to be placed in the following location: ConsoleManager/Apps/Marketing/Promotions/[YourCustomPromotionName].
- The .ascx must be named ConfigControl.ascx (although the code behind class must of course be unique).
- The control must inherit from Mediachase.Web.Console.BaseClasses.PromotionBaseUserControl.
- The control class must contain a serializable class called Settings. This class will contain the properties that will be used for setting the variable values for the formula (in the template/expression).
Example: the Settings class
Settings Class Example
[Serializable]
public class Settings
{
public int MinimumQuantity = 1;
public string ShippingMethodId = string.Empty;
public string RewardType =
PromotionRewardType.WholeOrder;
public decimal AmountOff = 0;
public string AmountType =
PromotionRewardAmountType.Value;
}- The control must override the SaveChanges() method from the base class. In addition, the DataBind() method should be overridden.
- The DataBind method should be used to set the properties in the control to the previously saved values (if applicable).
Settings
From the examples Settings class, there are several settings needed for most promotions. Note that you do not have to use these variable names. However, they are used in the built-in promotions and will probably be useful for the first promotions you create.
- RewardType. This is a string type and the types used in the engine are distinguished in the PromotionRewardType. There are three types: WholeOrder, AllAffectedEntries, EachAffectedEntry.
- WholeOrder applies a discount to the top-level properties of an order, namely the charge for a shipment or to the subtotal. Use WholeOrder for promotions which apply to either shipments or to adjustments to the subtotal.
- AllAffectedEntries calculates the total discount for affected SKUs as a whole. Example: when 2 or more of SKU x is purchased, $50 is deducted from the subtotal.
- EachAffectedEntry calculates a discount which is applicable to each applicable SKU in the cart. Example: When buying 2 or more of SKU x, get $20 off each SKU y purchased.
- AmountOff. Stores the % or amount off.
- AmountType. Determines whether the AmountOff property is a % or $ value. The PromotionRewardAmountType, which has enumerations Value and Percentage.
The Settings class should contain all of the properties set by the user in the control, and any other settings necessary for your promotion.
SaveChanges
Information for promotions is saved in the PromotionDto. The base class makes an instance of the particular promotions data available in the PromotionDto variable. You do not have to retrieve the promotion data explicitly in your control. The PromotionDto contains a table called Promotion. One row in the Promotion table represents the settings for a single promotion.
The SaveChanges method is called by ECF when the user selects the OK button at the bottom of a promotion definition. In the SaveChanges method, an instance of the Settings class, should be populated with the customers settings, for instance settings.MinimumQuantity = decimal.Parse(txtMinimumQuantity.Text);).
Example:populating an instance of Settings
Settings settings = new Settings();
settings.MinQuantity = Decimal.Parse(MinQuantity.Text);
settings.AmountOff = Decimal.Parse(OfferAmount.Text);
settings.RewardType = PromotionRewardType.EachAffectedEntry;
int offerType = Int32.Parse(OfferType.SelectedValue);
settings.AmountType = offerType == 1 ? PromotionRewardAmountType.Percentage : PromotionRewardAmountType.Value;In the SaveChanges method, the Setting class values should then be serialized, using the SerializeSettings method in the base class, and then saved in a Dto used to store promotion details.
Example: serializing Settings
PromotionDto.PromotionRow promotion = PromotionDto.Promotion[0];
promotion.Params = SerializeSettings(settings);You do not have to save the promotion settings explicitly, this is done by Commerce Manager. Note also that the promotion row has an OfferAmount and an OfferType properties, which may be duplicate to some of your Setting parameters.
Example: OfferAmount and OfferType properties
promotion.OfferAmount = Decimal.Parse(OfferAmount.Text);
promotion.OfferType = Int32.Parse(OfferType.SelectedValue);When saving a promotion, the expression also needs to be saved. The variable values which are set in the Settings class are used to customize the template/expression. Then, the customized expression is saved in the ExpressionDto as a row in the Expression table of the DTO. This will make more sense after creating your first expression.
Example: creating and saving the expression
// Create custom expression from template
string expr = base.Replace(base.Config.Expression, settings);
// Create or modify expression
ExpressionDto expressionDto = new ExpressionDto();
ExpressionDto.ExpressionRow expressionRow = base.CreateExpressionRow(ref expressionDto);
expressionRow.Category = ExpressionCategory.CategoryKey.Promotion.ToString();
expressionRow.ExpressionXml = expr;
if (expressionRow.RowState == DataRowState.Detached)
expressionDto.Expression.Rows.Add(expressionRow);
// Save expression
ExpressionManager.SaveExpression(expressionDto);DataBind
When the control renders in Commerce Manager, during the creation or editing of a promotion, the controls need to be initialized and set to the previously saved values, if applicable.
Example: binding the controls
if (Config != null)
{
txtDescription.Text = Config.Description;
}
if (PromotionDto != null && PromotionDto.Promotion.Count != 0)
{
PromotionDto.PromotionRow row = PromotionDto.Promotion[0];
object settingsObj = DeseralizeSettings(typeof(Settings));
if (settingsObj != null)
{
Settings settings = (Settings)settingsObj;
CategoryXFilter.SelectedNodeCode = settings.CategoryCode;
MinQuantity.Text = settings.MinimumQuantity.ToString();
//select the correct shipping method, if it still exists
if (ddlShippingMethods.Items.FindByValue(settings.ShippingMethodId) != null)
ddlShippingMethods.SelectedValue = settings.ShippingMethodId;
}
txtDiscount.Text = PromotionDto.Promotion[0].OfferAmount.ToString("N2");
ManagementHelper.SelectListItem(ddlDiscountType, PromotionDto.Promotion[0].OfferType);
}Note the following:
- The base class Config property gives you access to information about the expression definition.
- The base class PromotionDto property provides access to the promotion settings.
- The Settings object can be deserialized by calling the DeserializeSettings() method.
Creating the expression
The expression is the "template" for multiple versions of the same promotion. The expression, consists of an XML file with 6 subelements.
Example: an expression (template) with subelements
<Promotion sortorder="300">
<Type>[Unique name with no spaces or special characters]</Type>
<Name>[Name used for display purposes]</Name>
<Description>[Short Description]</Description>
<Group>[this must be one of the following values - shipping, entry, or order]</Group>
<Path>[relative path to the config control from one folder above Configs folder. For example : BuySKUFromCategoryXGetDiscountedShipping/ConfigControl.ascx</Path>
<Expression>[This is most of the config file. It consists of XAML which defines the promotion rules] </Expression>
</Promotion>Five of the six subelements require no further explanation. Note that all of these properties are available in the ConfigControl.ascx.cs as a base property called Config. The expression is a lengthy XAML statement that you will not edit directly. Instead, you will use a tool included with ECF, the Expression Editor.
When you are creating a promotion, you will generally want to use an existing promotion and modify its contents for your new promotion. These are the steps to accomplish this:
- Copy the XAML for the expression of an existing template, everything inside and not including the <Expression> open and close tags.
- Open ExpressionEditor. It can be found in BusinessLayer/Marketing/ExpressionEditor/bin/Debug/ExpressionEditor.exe.
- Paste the XAML into the expression text box.
- Click Edit Expression. The Rule Set Editor (a .NET tool) will appear with the expression in rule form.
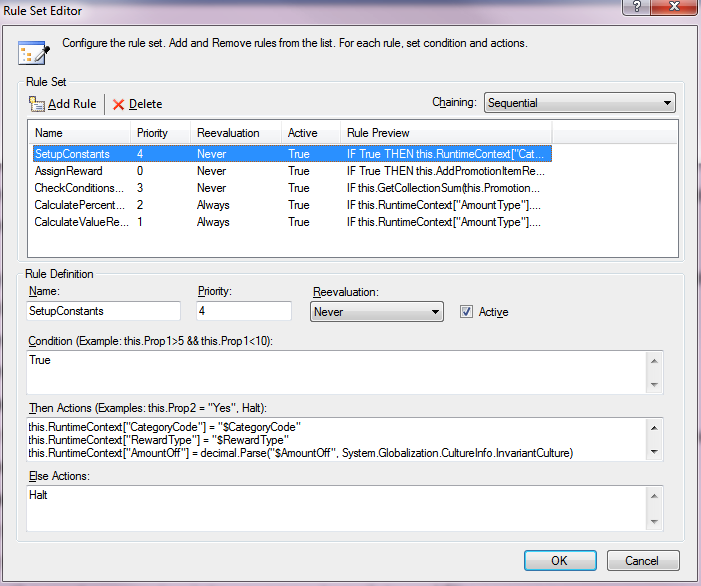
- Make changes to the expression (see below).
- Click OK for the Rule Set Editor, closing the window.
- Click Copy in the ExpressionEditor.
- Paste the next expression into your new template XML file.
Editing the rules
Before editing the rules there are a few important things to understand:
- Each rule is effectively an If..Then..Else statement, however its technically Condition..Then..Else. You provide what the If, Then, Else statements are to do. If the If/Condition statement is true, the Then statement executes; otherwise the Else statement executes.
- If at any point the keyword HALT is executed in an expression, the expression evaluation stops.
- The Rule Set Editor provides intellisense for the objects accessible to you.
- You can access the EPiServer Commerce API for any subsistence if needed.
- Each line, separated by a carriage return constitutes a different line of code (; is not required at the end of each line).
- From the RSE, when you type this., you are accessing the default object associated with the promotion rules, Mediachase.Commerce.Marketing.Validators.RulesContext.
- This object contains a lot of information about the order and current promotion context, including:
- CurrentCustomerContact
- PromotionCurrentOrderForm [for evaluating order promotions]
- PromotionCurrentShipment [for evaluating shipping promotions]
- PromotionTargetLineItem [for evaluating entry promotions]
- ShoppingCart [returned as a OrderGroup object, meaning it could be a PurchaseOrder or PaymentPlan also]
- The rules are executed in order, from highest priority (largest number) to lowest. - The general pattern you typically want to follow is:
- First rule should be assigning variables.
- Next rules(s) should be determining whether the conditions of the promotion are met and the promotion amount.
- The final rule should be creating a new PromotionItemRecord which indicates the type and amount of the promotion.
Assigning variables
Remember that the expression is the "template" for multiple versions of the same promotion. When you are assigning variables, you are assigning the promotion-admin-specified parameters.
Example: assigning variables
Name: SetupContants
Priority: 2
Condition: True
Then
this.RuntimeContext["RewardType"] = "$RewardType"
this.RuntimeContext["AmountOff"] = decimal.Parse("$AmountOff", System.Globalization.CultureInfo.InvariantCulture)
this.RuntimeContext["AmountType"] = "$AmountType"
this.RuntimeContext["MinOrderAmount"] = "$MinOrderAmount"
Else
HaltIn the If statement. If true will always return true which means the Then statement will always execute and the Else will never execute. Also note that, for this statement to execute first, all other rules must have a numerically lower priority. The name is not significant to the rules but can help you to know the purpose of the rule.
The $.. values, for instance ..= "$CategoryCode"), are the exact names of the parameters that are saved in your Settings class in the configuration control. When the following line is executed (part of the configuration control directions before), the template is made into a specific promotion:
// Create custom expression from template
string expr = Replace(Config.Expression, settings);Replace is a base class method which has two parameters: the expression and the Settings class instance for that promotion. The Replace class will look for all instance of the variable names from the Settings instance (with a $ in front of it) in the expression and replace them with the value from the Settings instance.
All of the values are set as strings in the expression instance. If a new promotion is created with the above variables, you should have a Settings class definition looking something like the example below.
Example: Setting class definition
[Serializable]
public class Settings
{
public string RewardType = PromotionRewardType.WholeOrder;
public decimal AmountOff = 0;
public string AmountType = PromotionRewardAmountType.Percentage;
public decimal MinOrderAmount = decimal.MaxValue;
}This means there is a one-to-one match between the variables in the Settings class and the variables you set in this first rule. If you create an instance of this promotion where the AmountOff is 5, the MinOrderAmount is 100j and the RewardType and AmountType are left as is, the Replace function will create an expression instance that will look like the example below.
Example: promotion expression instance
Priority: 2
Condition: True
Then
this.RuntimeContext["RewardType"] = WholeOrder"
this.RuntimeContext["AmountOff"] = decimal.Parse(5", System.Globalization.CultureInfo.InvariantCulture)
this.RuntimeContext["AmountType"] = "percentage"
this.RuntimeContext["MinOrderAmount"] = "100"
Else
HaltThe string instance created by the Replace method represents a specific version of this promotion. This value is saved in the database and used during promotion calculations. If you want to see this in action, retrieve the value of the Expression field in the Promotion database table for a particular promotion and load it into the Expression Editor.
Promotion condition test
It is possible to test whether the order meets the conditions of the promotion.
Example: testing the promotion conditions
Name: CheckOrderSubTotal
Priority: 1
Condition
this.PromotionContext.PromotionResult.RunningTotal < decimal.Parse((string)this.RuntimeContext["MinOrderAmount"], System.Globalization.CultureInfo.InvariantCulture)
Then
Halt
ElseThis rule in effect says If the order subtotal is less than the specified minimum order amount, halt the promotion evaluation as it does not apply. The end result is that no discount will be returned by the promotion engine in that case. If, however, the condition is false, meaning the subtotal is equal to or greater than the minimum order amount, there is an empty Else statement, resulting in that nothing is done and the next rule is executed.
AssignReward
This is the step where, if the rules have executed to this point, a promotion result needs to be returned. This is a PromotionItemRecord object. The parameter for the AddPromotionItemRecord most commonly used is a new PromotionItemRecord.
The constructor values for a new PromotionItemRecord are:
- The target entries/SKUs
- The affected entries/SKUs
- A new PromotionReward instance which has two parameters:
- The amount off value (a decimal)
- The amount type (percentage or value)
From the AddPromotionItemRecord returned PromotionItemRecord, the PromotionItem is assigned to the PromotionContext.CurrentPromotion, thus passing the promotion information back to the portion of the code that called the rules engine (StoreHelper.cs or CalculateDiscountActivity.cs) to be added to the cart.
Note that the [reduced] syntax PromotionItem = this.PromotionContext.CurrentPromotion is not quite intuitive. This statement is doing two things: adding a PromotionItemRecord to the current context, and setting the PromotionItem associated with that PromotionItemRecord to the current promotion. That PromotionItem contains the properties of the promotion from the database. Finally, the ValidationResult.IsValid = True statement indicates that the result is valid and should be applied.
Example: AssignReward
Name: AssignReward
Priority: 0
Condition
True
Then
this.AddPromotionItemRecord(new Mediachase.Commerce.Marketing.Objects.PromotionItemRecord(this.PromotionContext.TargetEntriesSet,
this.PromotionContext.TargetEntriesSet, new Mediachase.Commerce.Marketing.Objects.PromotionReward((string)this.RuntimeContext["RewardType"],
(decimal)this.RuntimeContext["AmountOff"], (string)this.RuntimeContext["AmountType"]))).PromotionItem = this.PromotionContext.CurrentPromotion
this.ValidationResult.IsValid = True
Else
HaltOther examples
Buy X, get Y free promotion
In this case, the PromotionContext.SourceEntriesSet.MakeCopy() method is called. The SourceEntriesSet and TargetEntries set properties are both PromotionEntriesSet types, which represent a collection of entries. When working with entry promotions, the SourceEntriesSet consists of all of the entries associated with the lineItems in an OrderForm.
The TargetEntries consists of one lineitem at a time, with the promotions tested against one LineItem entry at a time. With order promotions, the SourceEntriesSet consists of all of the LineItem entries associated with an OrderForm. With shipment promotions, the TargetEntries consist of all of the LineItem entries associated with a single shipment.
When the SourceEntriesSet.MakeCopy() method is called, it returns the subset of entries specified by the $EntryYFilter parameter. The $EntryYFilter variable is simply a delimited list of entry codes. You can use any special character (#,$& etc) to delimit the list of entries. See the ConfigControl for BuyXGetNofYatReducedPrice for an example of how to build this variable string.
Example: SetupConstants expression for the buy x, get y free promotion
Priority: 1
Condition: True
Then
this.RuntimeContext["EntryXSet"] = this.PromotionContext.SourceEntriesSet.MakeCopy(new string[] {"$EntryXFilter"})
this.RuntimeContext["EntryYSet"] = this.PromotionContext.TargetEntriesSet.MakeCopy(new string[] { "$EntryYFilter"})
Else
HaltPromotion condition test
This example uses a method of the RulesContext object, GetCollectionSum. In this case, we are using it to find the total quantity of SKUs from the SourceEntriesSet where the CatalogNodeCode property of the entries is equal to the category code associated with the promotion. If its equal to or greater than the variable minimum quantity, the promotion applies.
The third parameter of the GetCollectionSum allows you to pass in a code expression to use as a filter. The code expression is passed in as a string and turned into a System.CodeDom.CodeExpression. The Windows Workflow Rules engine can then use that expression to filter the IEnumerable Entries collection.
The RulesContext offers a number of methods to allow you to do more efficient evaluations of the cart for promotion condition checks like this using CodeExpressions to filter, validate, or count qualities of the cart.
Example: Promotion condition test
Name: CheckConditionsMet
Priority: 2
Condition
this.GetCollectionSum(this.PromotionContext.SourceEntriesSet.Entries, "Quantity", "this.CatalogNodeCode.ToString().Equals('" + this.RuntimeContext["CategoryCode"].ToString() + "')") < decimal.Parse(this.RuntimeContext["MinQuantity"].ToString()) || this.PromotionCurrentShipment.ShippingMethodId.ToString() != this.RuntimeContext["ShippingMethodId"].ToString()
Then
Halt
ElseThere are numerous other promotion examples included in the ECF source code. Review these to better understand other custom promotion options. Another way to get ideas about how to implement your promotion can be found by creating promotions using the Build Your Own Discount option available for entry and order promotions. Create a promotion which includes criteria or rewards similar to your design and then review the expression from the Expression database table in the Expression Editor - it will often provide vital clues for how to complete your promotion.
Debugging tips
Once you have created you promotion and are testing how it works with you environment, there are a few tips that will expedite your debugging:
- Turn off marketing caching during testing. These settings are in the cache node of the ecf.marketing.config file in the Configs folder of the site. Set all of the caching to 0:0:0.
- The execution of the rules in the rules engine cant be debugged directly. However, there are several locations where breakpoints will allow you to determine the inputs and outputs into the rules engine for your promotion.
- Place a breakpoint in BusinessLayer/Marketing/MarketingRuleValidators/RulesExprValidator.cs, in the getter for the RuntimeContext property. This will allow you to see exactly what parameters are being passed into the rules engine from the promotion settings, which were saved by the user in defining the promotion in Commerce Manager. This is a dictionary that is used to pass in the promotion definition Settings variable values into the rules engine.
- See also BusinessLayer/CommerceLib/Marketing/MarketingContext.cs, EvaluatePromotions(PromotionContext context, PromotionItemCollection promotions, PromotionFilter filter) method. This is called by the workflow activity CalculateDiscountActivity.
- See also BusinessLayer/ActivityLibrary/Cart/CalculateDiscountActivity.cs, in the catch portion of the try statement of the Execute method. A lot of errors are caught and thrown without the exception details in the workflow. For debugging, add an (Exception ex) to the catch and then inspect the errors.
Last updated: Mar 31, 2014
