Meta-class references
Business Foundation (BF) supports referencing among meta-classes, which is useful when you create relations between different types of business objects. You can create the following types of references:
Note: When you create meta-class references, remember that you can modify a meta-model only in Design mode. See the MetaClassManager class section.
Creating a 1-N reference
The 1-N reference type creates a reference between two meta-classes.
Note: Define the TitleFieldName property of the MetaClass class with the correct string field name if you want to create a reference to this meta-class.
The following example shows how to create a reference between the two meta-classes called Project and Task.
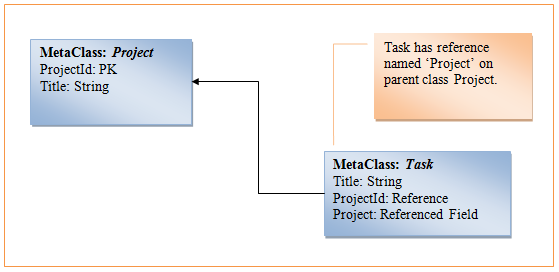
To create a reference to the parent meta-class, call the CreateReference method of the MetaClass class, passing parent meta-class, reference name, friendly name and is nullable flag.
Example: Creating a reference between Project and Task
// Open the meta-model edit scope
using (MetaClassManagerEditScope scope = DataContext.Current.MetaModel.BeginEdit())
{
// Create reference
DataContext.Current.GetMetaClass("Task").CreateReference(
DataContext.Current.GetMetaClass("Project"), "Project", "Project", true)):
// Save Changes
scope.SaveChanges();
}The CreateReference method adds two fields to the meta-class:
- Reference Id. Reference on the parent primary key, named [ReferenceName]Id, which is used to get/set the reference to the parent object.
- Reference Title. A read-only referenced field property to the parent title, named [ReferenceName], which is used to get the title of the parent object.
When you update Reference Id, Reference Title is automatically updated.
Note: More than one reference can be created between two meta-classes.
Creating a reference field
After creating a reference, add any field from the parent meta-class as Reference field.
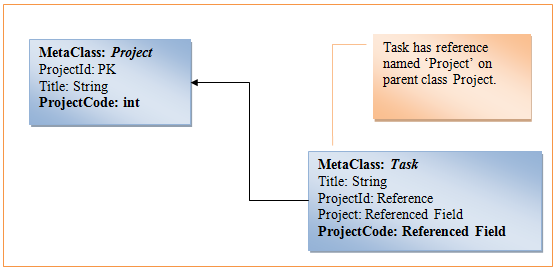
Referenced fields are read-only. If a reference is not set, the reference field returns null. When you update the Reference Id, Reference Title is automatically updated.
To add a referenced field to a meta-class, call the CreateReferencedField method of the MetaClass class, passing the reference field to the parent meta-class, and the parent field and field name.
Creating a back reference
After creating a reference in the parent meta-class, you can create a Back reference field on an existing reference. The back reference field returns a collection of child objects that have a reference to the current object.
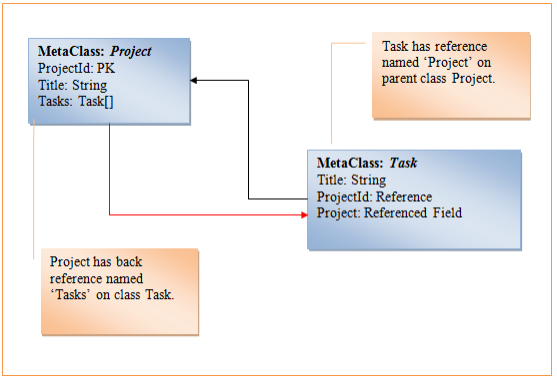
To add a back reference field, call the CreateBackReference method of the MetaClass class, passing reference field and field name.
Creating an N-N reference
The N-N reference type is also called a bridge, which is meta-class with two reference on class #1 and class #2.
Note: Remember to define the TitleFieldName property of the MetaClass class in both meta-classes.
The following example shows how to create a bridge between the two meta-classes Project and Union.
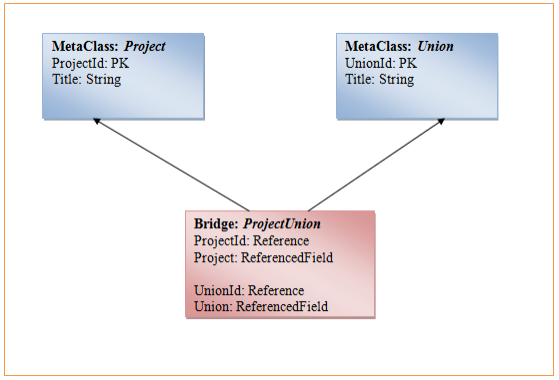
Call the CreateBridge method of the MetaClassManager class, passing class #1 and class #2 to create a bridge between the two meta-classes. The bridge meta-class will be visible in the collection of meta-classes like the original meta-class, but it will have an IsBridge property with the value "true". You can add a meta-field or delete a bridge meta-class like any other meta-class.
Creating an aggregation reference
Aggregation is slightly more complex than references. You typically use it to enable the parent entity object that has a collection of child entity objects, where one element is marked as default. The default children entity object is loaded when the parent object is loaded, and will be available from the property. The properties of children entity objects can be modified and will be saved when you save the parent object. When you delete a parent object, all aggregated objects are automatically removed.
Note: Be careful to define the TitleFieldName property of the MetaClass class with the correct string field name if you want to create an aggregation reference to this meta-class.
The following example shows the Client and Address meta-classes, where the Client meta-class aggregates the Address meta-class. The client has many addresses but one is marked as default, and is available from the Client.Address property. The Address property returns an entity object, and you can update the default address properties as client properties. When you save Client, the default Address is automatically saved.
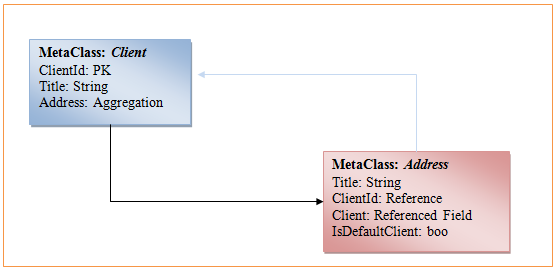
To add an aggregation to a meta-class, call the CreateAggregation method of the MetaClass class, passing the children meta-class. CreateAggregation adds a new meta-field to a parent meta-class, which can set and update an aggregated object.
Example: Creating an aggregated reference
public MetaField CreateAggregation(string name, string friendlyName, string childMetaClassName,string elementContainerRefFieldFriendlyName,string defaultElementFieldFriendlyName)
{
MetaField retVal = this.MetaClass.CreateAggregation(childMetaClassName, name, friendlyName,
elementContainerRefFieldFriendlyName,
defaultElementFieldFriendlyName);
return retVal;
}Last updated: Oct 12, 2015
