Securing edit and admin user interfaces
Introduction
This document contains general instructions on how to secure the user interfaces in CMS, including instructions on how to secure the UI folder (which contains the EPiServer editing and administration interfaces) and how to ensure that the application will continue to work even if the UI folder is moved to a new location.
General recommendations
Below are some recommendations on how to prevent unauthorized users to access the edit and admin user interfaces in CMS:
- Have separate servers for UI and public web, where the UI server is on an internal protected network.
- Remove access to editing and administration interfaces
- Remove access to any custom Edit/Admin plug-ins from the public facing server (for example by removing the files).
- If it is not possible to have separate servers, it is recommended to have separate bindings in IIS for the web and the UI and to use SSL on the UI-binding.
Removing access to editing and administration interfaces
Follow the description below to make the edit/admin user interfaces unavailable on a publicly facing server.
In web.config, both for <location path="EPiServer"> and <location path="EPiServer/CMS/admin">, remove any allow roles (WebEditors, WebAdmins, Administrators and additonal ones) so that the <authorization> sections only contain the following:
<authorization>
<deny users="*" >
</authorization>Securing the editing and administration interfaces
EPiServer CMS allows relocation of the edit and admin folders to custom folder names and configurable HTTP ports, to make it harder for intruders to try to access sensitive resources.
Renaming the UI Folder
- Change the uiUrl attribute of the applicationSettings element in the web.config to a custom name:
uiUrl="~/newuipath/"
If you want to secure the UI folder on another port other to that the site is running on, add an absolute URL including a port other than 80 (or a port the application is running on) as shown below. Setting uiUrl to a custom host and port is not recommended for multi-site setups since each site have custom domains. Consider having a separate editing server instead and remove access to editing and administration interfaces on publicly facing server.
uiUrl="http://localhost:8888/newuipath/" - Change the UI provider virtual path attribute from the previous value, for example from "~/EPiServer" to "~/newuipath".
<add virtualPath="~/newuipath/" physicalPath="Modules\_Protected" name="ProtectedModules"type="EPiServer.Web.Hosting.VirtualPathNonUnifiedProvider, EPiServer.Framework" /> - Change the location element path attribute from UI to newuipath see below for an example:
<location path="newuipath"> - Change the location element path attribute from UI/admin to newuipath/admin:
<location path="newuipath/admin"> - Change the protected modules root path to newuipath:
<episerver.shell>
<publicModules rootPath="~/modules/" autoDiscovery="Modules" />
<protectedModules rootPath="~/newuipath/"> - Add a specially designated (and restricted) port for access in the Internet Information Services (IIS) for the site (used for the UI folder in the step 1 above, port 8888 is used for uiUrl). Access to this port could then be restricted (this step can be omitted if you only want to change the folders).
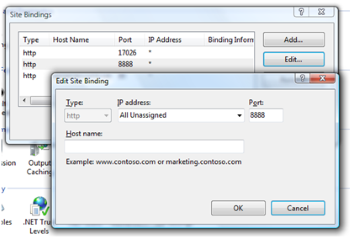
Add support for SSL
Using SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to secure the website and/or UI folder is possible, see the information in the following links:
Last updated: Feb 23, 2015
